How to Draw Points and Lines in Java
A Deep Dive Into CustomPaint in Flutter
Exploring CustomPaint and CustomPainter to add a Canvas to your app
![]()

If you are starting out with Flutter, you may not have heard of or used the CustomPaint widget a lot. Most widgets in the framework take care of common features and functionality and even when they don't, you rarely need to draw it yourself since customizations like rounding corners, changing opacity, substituting colors, etc. are all easily doable.
However, when it comes to more custom design — for example an arrow drawn from one place to the other, a fancy loading animation, or a ticket receipt that looks like a ticket stub — you may need a way to render shapes that simple widgets cannot provide.
Introducing the Canvas
Most if not all UI frameworks provide a Canvas API — a way for drawing custom graphics that does not involve existing UI components. A Canvas is pretty much what is sounds like: you can draw lines, shapes, curves, etc. using the Paint (color, stroke, …) you prefer. This allows you to render custom components which can be exactly the shape and size you want them to be.
In Flutter the CustomPaint widget provides a Canvas for us to use. We use the CustomPainter class to actually draw our graphics on the screen. The three main things to take a look at are: CustomPaint , CustomPainter , and the Canvas class. Let's start.
The CustomPaint Widget
As aforementioned, the CustomPaint widget supplies the Canvas while the CustomPainter is where we write logic for painting. Let's look at purely the widget first.
There are three things important in the widget parameters:
-
child -
painter -
foregroundPainter
The painter and foregroundPainter are both CustomPainters which define what is drawn on the canvas. However, the instructions from the painter are drawn first. After that, the child is rendered OVER the background. And finally, the instructions from the foregroundPainter are drawn over the child .
In summary: The widget builds three layers using these three parameters in a stack-like format. The lowest layer is the drawing by the
painter, then thechild, and finally theforegroundPainterdrawing.
By default the size of the widget is the child size. When the child is null, it uses the value of the size parameter given to it.
Looking Into The CustomPainter
Now that we have a CustomPaint widget which will provide the Canvas, we need to actually paint something. To do this, we subclass the CustomPainter class to create our own.
There are two major functions:
-
paint(): This is where we supply instructions for painting on the canvas. -
shouldRepaint(): When a newCustomPainterinstance is provided, we can decide if we need to repaint the canvas based on the new parameters.
The paint() function supplies the actual Canvas instance which we can use to invoke the drawing functions. It also gives us the size of the canvas which is either the child size or supplied through the size param.
Let's look at the actual drawing logic by exploring the Canvas class next.
Drawing On The Canvas
What has been shown till now should be familiar to most people who who have used the CustomPaint widget a few times. In this section we will go into drawing things on a Canvas and all the possibilities that it offers.
All the drawing mentioned here will be done inside the paint() method of the CustomPainter .
Common classes used in painting
Paint
The paint class stores attributes related to painting or drawing objects on the screen. Here are a couple of important attributes:
- color: Sets color of painting
- strokeWidth: Thickness of each line stroke drawn
Rect
A Rect class creates a virtual rectangle with a width and height usually to draw an actual rectangle or set bounds for a shape inside. There are multiple ways to create a Rect such as:
Path
There are functions in the CustomPainter that help us draw common shapes such as circles and rectangles. However, when we need to draw custom shapes, paths allow us to trace out a custom shape.
Let's start drawing
Points and lines
Points (circles) and lines can be drawn on the canvas using the canvas.drawCircle() and canvas.drawLine() method respectively.
In the canvas.drawCircle() method, we supply a position to draw the circle at, the radius of the circle, and the paint attributes for painting the circle.
This pretty much just gives us a point at the center of the screen:
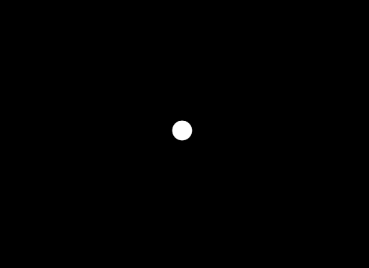
Here, we draw a line across the screen instead. We supply two points to draw the line between and the paint attributes. The first point is the left of the screen along half the height going towards the second point, which is at the same height on the other side of the screen.

Coloring the canvas
To fill the entire canvas with a color, we can use the canvas.drawColor() function which colors the entire canvas with a color.
The BlendMode defines how the color is painted over the existing elements on the canvas.
Adding text
Text can be rendered on the canvas as well — using the canvas.drawParagraph() method.
This requires quite a lot more setup than we're used to using the Text widget.

There is also a TextPainter class which can help simplify this, more information can be found here.
Drawing an arc
We can draw an arc of a circle using the canvas.drawArc() method. This makes it easy for us to create Pacman:

Drawing a path
As mentioned in the earlier section, the Path class allows us to create custom shapes. Once created, the path can be drawn on the canvas using the canvas.drawPath() method.
Muhammed Salih Guler did a better job at explaining how paths work than I can, I recommend checking that out here:
This article summarized the basics of the CustomPaint widget. Future articles will dive into more complex topics such as Shaders , BlendModes , etc.
On A Personal Note
My best use of the CustomPaint widget lies in creating generative art in Flutter. I use the widget to create procedurally generated artworks like this one:
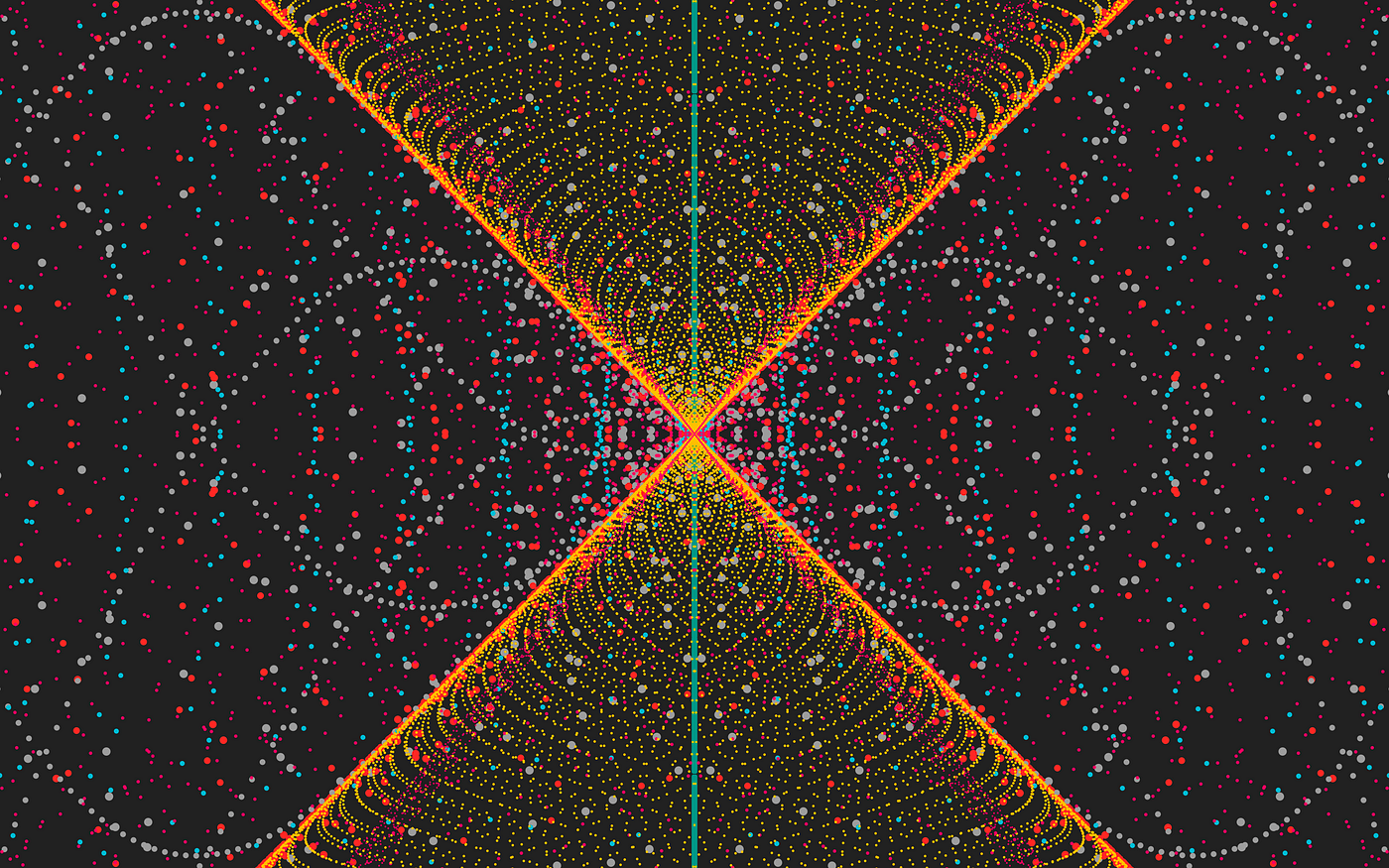
If you're interested, be sure to take a look on Instagram or Twitter for seeing more of the same.
That's it for this article! I hope you enjoyed it, and be sure to follow me for more Flutter articles and comment for any feedback you might have about this article.
Feel free to check out my other profiles and articles as well:
How to Draw Points and Lines in Java
Source: https://medium.com/flutter-community/a-deep-dive-into-custompaint-in-flutter-47ab44e3f216
0 Response to "How to Draw Points and Lines in Java"
Post a Comment